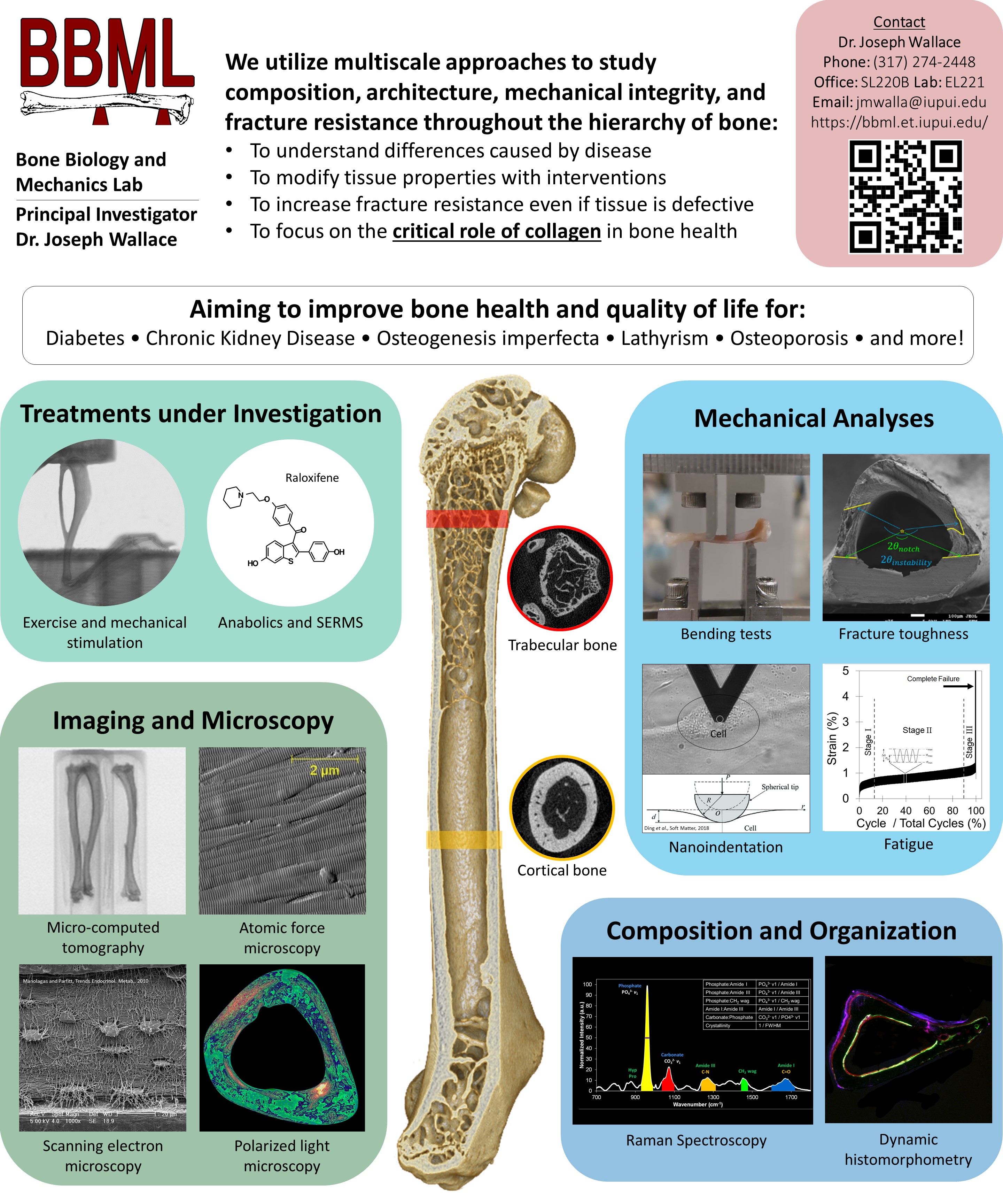
General Information on Current PI-Funded Grants
NIH/NIAMS R01: Targeting collagen as an interventional approach to improve bone material properties
Principal Investigator: JM Wallace
07/05/2018 – 05/31/2024 (NCE)
Mechanical loading and pharmaceutical interventions both improve bone mechanical properties, but there is a critical gap in our understanding of the role that collagen plays in mediating these effects. This gap in knowledge by which collagen processing, organization, mineralization, and hydration change with combined load and drug treatment (raloxifene, RAL) is a critical impediment to the development of combination therapies that increase fracture resistance by targeting tissue moieties other than mineral. The overall objective of this study is to elucidate how mechanical loading combined with RAL can modify newly forming and pre-existing bone to decrease fragility. The central hypothesis is that in addition to changes in mass and mineral, collagen-modifying effects exist for both loading and RAL, the combination of which interactively improve mechanical integrity beyond the effects of either monotherapy. This work will challenge the mineral/mass/architecture-centered dogma for reducing fracture and provide new ways to improve skeletal deficits by altering tissue quality.
NSF/CMMI LEAP-HI: Engineering new solutions to reduce the burden of skeletal fracture
Principal Investigators: JM Wallace, TH Siegmund (Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University), J Howarter (Materials Engineering), LR Pyrak-Nolte (Physics, Purdue University), MR Allen (Anatomy, Cell Biology, and Physiology, IU School of Medicine)
06/01/2020 – 05/31/2024
Long-standing strategies have focused on reducing bone fracture risk by maximizing bone mass/density, but fracture is still a critical public health issue. A transformational change requires a fundamental shift to engage engineering principles that combine structural geometry with material. Innovative interdisciplinary team integration driven by engineering science is addressing the concept of enhanced bone hydration as a novel and promising pathway to reduce bone fragility. This collaboration is forming a sustained team approach to address the question: What are the biomechanisms through which hydration alters local and tissue-level deformation and provides long-term toughening mechanisms to positively influence bone fracture resistance?
VA Merit: Improving bone mass and quality in comorbid diabetes and chronic kidney disease
Principal Investigator: JM Wallace
01/01/2023 – 12/31/2026
Diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) consistently rank among the top ten chronic conditions in the US in terms of prevalence and mortality. Both diseases cause a significant increase in fracture risk and fracture-related mortality due to skeletal deficits that worsen with age of disease onset and duration. While persons with diabetes are 33% more likely to present with CKD, diabetes and CKD comorbidity is twice as common in our veterans. Despite their increasing comorbidity and well-established detrimental impacts on the skeleton, their skeletal interaction remains under-explored. Treatment for skeletal disease typically address deficits in either bone mass or tissue quality, which may be insufficient in cases of combined CKD and diabetes where there are known deficits in both. The objective of this study is to investigate skeletal interactions between diabetes and CKD and identify effective combination skeletal treatments. The central hypothesis that increasing bone mass while concurrently improving tissue quality using combined therapies will increase bone mechanical strength, improve fracture resistance, and reverse adverse skeletal effects of early and late-stage diabetes+CKD. Combining treatments in comorbid disease models will provide alternative ways to make bone stronger and more resistant to fracture in the at-risk veteran population.
NIH/NIAMS R01: How bisphosphonates affect bone matrix and remodeling: implications for atypical femoral fractures
Principal Investigators: JM Wallace, RD Ross (Anatomy and Cell Biology, Rush University Medical Center), TL Andersen (Clinical Research, University of Southern Denmark)
05/12/2023 – 03/31/2028
Atypical femoral fractures (AFFs) are a rare but devastating side effect of long-term bisphosphonate (BP) treatment. AFFs are atraumatic or low-energy fractures with distinguishing radiologic features, including a transverse orientation and a lack of comminution. Despite the relatively low prevalence of AFFs, public awareness has considerably depressed osteoporosis medication adherence. The mechanisms driving BP associated AFFs remain elusive and several mechanisms have been proposed, including impaired bone remodeling, altered bone matrix maturation, and the accumulation of tissue microdamage. While the effects of BPs on osteoclasts are well-described, the mechanisms driving suppressed bone formation are not well understood. Similarly, while bone from AFF patients has altered matrix composition, whether this is secondary to suppressed remodeling or a direct effect on matrix maturation is unclear. Our central hypothesis is that BPs degrade skeletal integrity by affecting both bone formation initiation and matrix maturation. We will utilize an innovative preclinical model and leverage the expertise of a highly qualified research team to address critical questions associated with AFFs. If successful, we will further our understanding of the effects of BPs on the skeleton by disentangling the effects of BPs on bone formation initiation and matrix maturation, identifying factors that contribute to BP-induced loss of fatigue life and investigating a novel rapid treatment option for patients at risk for AFFs.
NIH/NIDDK R01: Uremic toxins and osteocyte dysfunction in CKD
Principal Investigators: JM Wallace, SM Moe(Nephrology, IU School of Medicine), MR Allen (Anatomy, Cell Biology, and Physiology, IU School of Medicine)
Scored at 9% in June 2023
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects over 20 million individuals in the US and as CKD progresses, the risk of hip fractures increases by 2 to 5-fold. Renal Osteodystrophy (ROD), the bone component of CKD-Mineral Bone Disorder is complex with both high and low bone turnover and bone quality changes, and remains a treatment challenge. Over the past 25 years, the therapeutic focus has been to lower the PTH level but this has not resulted in a change in the fracture rate. This implies that there are factors in CKD that are additive to PTH in inducing bone fragility. Recent studies in patients without CKD have identified the importance of the gut derived uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate (IS) that accumulates due to reduced renal clearance. Indoxyl sulfate is a ligand for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) important in detoxification of toxins and the promotion of multiple aging and bone phenotypes. In our rat model of CKD that parallels the human bone phenotype, our preliminary data demonstrated the oral administration of inulin, a fermentable dietary fiber, alters the gut microbiota and reduces serum levels of IS. This dietary intervention led to higher bone volume, decreased osteoclast number, and decreased cortical porosity. Using an osteocyte cell line for a model of osteoblast to osteocyte differentiation we also demonstrated that indoxyl sulfate increased AhR activity and altered genes important in osteocyte differentiation, function and mineralization. Based on these data, we propose the hypothesis that impaired bone quantity and quality in CKD is due to the interaction of the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate on osteocyte function mediated through aryl hydrocarbon signaling. These studies will determine the role of IS and AhR signaling in the osteocyte dysfunction of CKD, offering novel targetable mechanisms to improve bone quantity and quality and prevent fractures.